
|
|
Lab Description

Students will learn
how to put "principles into practice" in the
Computer Networks Lab.
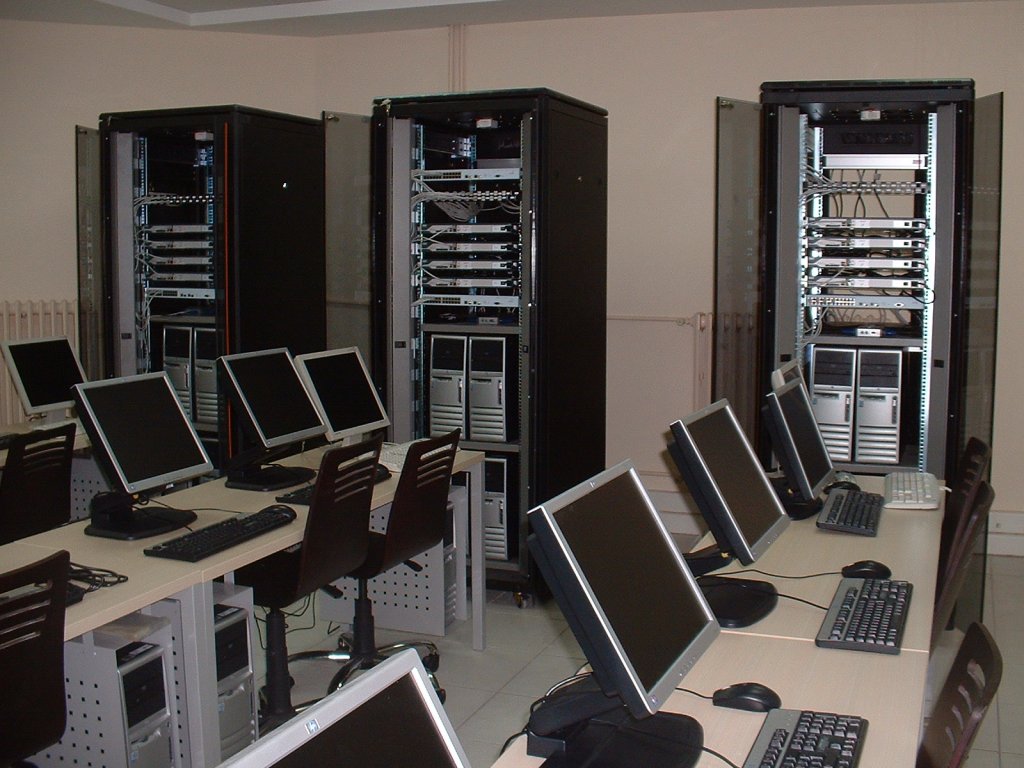
The lab is a miniature version of the
Internet. The available equipment is sufficient to emulate many
traffic scenarios found on the real Internet and to teach TCP/IP
protocols and data communication to students, and to give them
hands-on experience on networking.
The lab has modular
Internet rack
equipment. Each rack has 4 Cisco 2811 Integrated Services Routers, a
3Com switch, 4 PCs as internet hosts, 4 switches, 1 KVM switch and
its set (LCD monitor, keyboard, and mouse), cables and connectors.
One set of
rack equipment is used by 4 students in lab experiments.
Currently there are 6 racks in the lab, and since the design of the
lab is modular and scalable, it can be easily extended if it is
needed in the future.
The lab experiments cover some
of the important Internet protocols, including IP, ARP, ICMP, UDP, TCP, routing protocols (RIP, OSPF, BGP), and
application-level protocols (DNS, HTTP, FTP, TELNET). In addition to an
in-depth study of the Internet protocols in real network settings, you will
gain hands-on experience working on networking equipment and acquire useful
networking skills. By putting computer networking into practice, this lab
aims to teach how network protocols work and how networked systems interact.
There are about 12 lab sections and and 10 different labs. Each lab consists of a
prelab, lab session, and a postlab report. Prelab will
be individual work. The lab exercises and postlab reports will be completed
in groups of 4. The lab exercises are completed without supervision and
require on the average 3 hours of work.
Lab Materials and
References
 |
Mastering Networks: An Internet Lab Manual,
J. Liebeherr, M. E.
Zarki,
Addison-Wesley, 2004, ISBN: 0-201-78134-4. (Lab book) |
 |
TCP/IP
Tutorial and Technical Overview, A.Rodriguez, J.Gatrell, J.Karas,
R.Peschkem, IBM Redbook (available over the Net). |
 |
TCP/IP Tutorial: TCP/IP
networking principles that form the basis of discussion for many of the
laboratories. |
 |
Links in the Lab
Manual |
Tentative Lab Schedule
|
W |
Dt |
Lec |
Lectures |
LABs |
| |
|
|
Intro |
|
|
2 |
18/2 |
Lab 1 |
|
Lab 0: Introduction to the
Lab, Networking Tools and Linux: Objectives of the
Lab Experiments, Experiments, Lab Activities, Procedures and
Grading, Lab Hardware and Software, Linux
Introduction to the Internet Lab
Wireshark Lab: Getting Started (Optional
study at home)
CISCO
Packet Tracer v4.1: Simulation and visualization program
designed for networking novices.
Start to go over networking tutorials of this simulation
program as you learn new topics in class and also study in
advance during the semester. It is an exiting and very
useful tool to learn networking concepts, network devices
and their configurations at home without going to a real lab
environment.
Readings / References:
TCP/IP Tutorial |
|
3 |
25/3 |
Lab 2 |
App. |
Lab 1: Introduction to the Internet Lab: Becoming familiar with the lab
equipment, introduction to ethereal and tcpdump, basic Linux commands.
Readings / References
|
|
4 |
3/3 |
Lab 3 |
|
Lab 2: Single
Segment IP Networks: 1. Using Filters in tcpdump,
2. Using Filters in ethereal, 3. ARP-Address Resolution Protocol, 4. The
netstat Commond, 5. Duplicate IP Addresses,
6. Changing Netmasks, 7. Static Mapping of IP Addresses and Host Names,
8. Experiments with FTP and Telnet |
|
5 |
10/3 |
Lab 4 |
|
TCP/UDP Socket Programming:
Example
Programs Introduction to TCP/UDP socket programming and
understanding reliable connection-oriented and unreliable
connectionless services provided by the transport layer
protocols, TCP and UDP respectively. Compiling, running, and
modifying simple TCP/UDP Java client/server applications on
a computer and then porting the same client/server
applications to 2 (one server/one client) and 3 (one
server, 2 clients) computers. |
|
6 |
17/3 |
Lab 5 |
Transport |
DNS and
HTTP and
ethereal Labs from the main text book
DNS
and HTTP Prelab
Questions |
|
7 |
24/3 |
Lab 6 |
|
TCP from the main textbook
TCP Prelab Questions |
|
8 |
31/3 |
Lab 7 |
|
TUTORIAL:
Introduction to
Routers: What is a Router? Hardware and Software Components of a
Router, CISCO 2800 Series and 2811, CISCO Internet Operating System (IOS)
Networking Tools:
Network Programs, Packet Capturing and Analysis, Network Simulation,
Network Management
Start to use CISCO Packet Tracer 4.1 to learn CISCO IOS
commands and to build and simulate networks
Cisco IOS and Configuring Cisco
Routers |
|
8 |
7/4 |
|
Midterm |
|
|
9 |
14/4 |
Lab 8 |
Network |
Lab 3: Static
Routing (Part 1): Configuring a Linix PC as
an IP Router, Configuring a Cisco Router, Finalizing and
Exploring the Router Configuration, Proxy ARP
Understanding IP Addressing |
|
10 |
21/4 |
Lab 9 |
|
Lab 3: Static
Routing (Part 2): ICMP Route Redirect,
Routing Loops, Netmasks and Routing |
|
11 |
28/4 |
Lab 10 |
|
IP Lab from the
main text book
IP Prelab Questions |
|
12 |
5/5 |
Lab 11 |
Data Link
LANs |
Lab 4: Dynamic Routing Protocols (RIP, OSPF, BGP): Routing protocols
RIP, OSPF and BGP; count-to-infinity problem in RIP; hierarchical
routing in OSPF; setup of autonomous systems in BGP
Readings / References: IBM Red Book, Chapter 4 |
|
13 |
12/5 |
Lab 12 |
|
Lab 6: LAN Switching: LAN switching in Ethernet networks; forwarding of
Ethernet frames between LAN switches/bridges; spanning tree protocol for
loop free routing between interconnected LANs
Lab 7: NAT and DHCP: Setup of a private network; dynamic assignment of
IP addresses with DHCP |
|
14 |
20/5 |
|
Lab Final |
|
|
